Quick Facts:
- Underground storage caverns are used to store very large quantities of unrefined petroleum and natural gas.
- These underground caverns are cavities that have been “mined” out of naturally occurring salt domes.
- Approximately 7% of total underground natural gas storage capacity is in Salt Caverns.
- There are approximately 36 underground natural gas salt cavern facilities in the United States, most, but not all, are located in the Gulf Coast States.
- For total gas capacity of all types of reservoirs, aquifers and caverns: Depleted reservoirs account for 78.2%, aquifers at 14.8%, and caverns at 7%.
Overview
Most underground storage of natural gas occurs in depleted natural gas reservoirs. Underground storage fields have also been created by leaching underground caverns in salt domes. The most notable example of this storage method is the National Strategic Petroleum Reserve, which stores the nation’s reserve of crude oil for use in national emergencies. Salt domes are suited for this purpose because they are dry and geologically stable, allowing crude oil and other petroleum substances to be safety isolated and stored in large quantities.

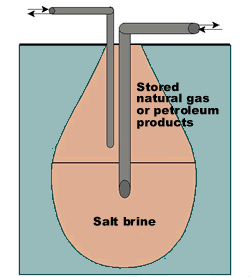
To create an underground cavern in a salt dome, a hole is drilled from the surface down to the salt dome, and water is injected to dissolve the salt and create the storage space. The salt solution is pumped out until the required cavern volume is achieved. The cavern is then filled with crude oil or other petroleum-based substance, such as ethylene or propylene.
Stored product is extracted from salt caverns by pumping brine into the cavern. Because the brine is denser than the stored product, it forces the stored product out of the cavern. Also, because of density differences, the brine does not mix with the stored product. When brine is removed from the cavern, it is stored in specially-constructed brine storage ponds and can be used over and over again, minimizing environmental impact.
A simplified schematic of a typical salt dome cavern is shown on the right.
Regulation of Underground Storage Caverns
Underground Natural Gas Storage caverns are regulated by 49 CFR Part 192.
Underground Storage Caverns: Where can I find more?
- PHMSA Community Liaison Services
- Storage of Natural Gas
- Code of Federal Regulations 49 CFR Part 192 – Transportation of Natural Gas
- Code of Federal Regulations 49 CFR Part 195 – Transportation of Hazardous Liquids by Pipeline
Date of Revision: 01112018
